Blasticidin S Hydrochloride (syn: Blasticidin S HCl) is a peptidyl nucleoside produced by several species of Streptomyces that was first isolated from S. griseochromogenes in 1958. Blasticidin S inhibits protein synthesis and is active against bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and tumor cells. The compound is used as a selection antibiotic for both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, and a marker for strain manipulation. Blasticidin S Hydrochlorde is soluble in water and acetic acid.
We also offer:
This product is considered a dangerous good. Quantities above 1 g may be subject to additional shipping fees.
| Mechanism of Action |
Blasticidin S HCl inhibits protein synthesis in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by binding to the ribosomal P-site which strengthens tRNA binding and slows down and prevents subsequent peptide synthesis. Mechanisms of Resistance: Resistance to Blasticidin S is conferred by bsr, BSD, and bls resistance genes isolated from Bacillus cereus K55-S1, Aspergillus terreus, and Streptoverticillum spp, respectively. The bsr resistance gene is a 420 bp fragment and encodes a 15 kDa Blasticidin S deaminase which catalyzes the reaction of blasticidin S to deaminohydroxyblasticidin S. Deaminohydroxyblasticidin S is a biologically inactive derivative of blasticidin S and does not interact with or inhibit prokaryotic or eukaryotic ribosomes. The BSD resistance gene is a 393 bp fragment and also encodes a Blasticidin S deaminase enzyme which catalyzes a similar reaction to the BSR deaminase. A study by Kimura et al. found the transfection frequency with bsd to be 80X greater than with bsr when using FM3A cells. The bls gene resistance gene encodes an acetyltransferase which interacts with acetyl-coenzyme A and prevents blasticidin S from inhibiting protein synthesis. |
| Spectrum | Blasticidin S HCl is biologically active against susceptible mammalian and prokaryotic cells. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Blasticidin S HCl can be used as a selection agent after transformation of prokaryotic (bacterial) cells, namely E. coli. Optimal Blasticidin S HCl selection concentrations range from 25 - 100 µg/mL and should be tested for each experimental condition. Selective media containing Blasticidin S HCl should contain a low salt concentration (<90mM) and pH ≤7 to avoid Blasticidin degradation. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Blasticidin is selection antibiotic for both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Resistance to Blasticidin is conferred by the following genes:
1) bsr (blasticidin resistance), from Bacillus aureus, which codes for blasticidin-S deaminase. 2) bls (blasticidin S acetyltransferase), from Streptoverticillum spp. 3) BSD (blasticidin S deaminase), from Apergillus terreus. Researchers used Blasticin S (TOKU-E) to select for transfected AS-B145 and BT-474 cells, which are human breast cancer stem/progenitor cells, a subpopulation of cancer cells that are involved in tumor initiation, resistance to therapy, and metastasis (Lu et al, 2016). Preparation note: Prepare stock solutions at 5-10 mg/ml in water or 20mM HEPES and store at 4°C (short-term) or -20°C (long-term). Optimal selection concentration depends on the cell line, growth conditions, media, reagent quality and potency, manufacturing lot, cell density, cell metabolic rate, cell cycle phase, and plasmid properties. A kill curve should be performed for each experimental system to determine the optimal working concentration. For more information on relevant cell lines, culture medium, and working concentrations, please visit the TOKU-E Cell-culture Database. |
| Cancer Applications |
Ring finger protein 43 (RNF43) is known for its role in negative regulation of the Wnt-signaling pathway in cancer. However, the function in DNA double-strand break repairs has not been investigated. Researchers used cellular models (lymphoblast cell line, DT40 along with mouse embryonic fibroblast) to study DNA double-strand break (DSB) repairs. They used Blasticicin S HCl from TOKU-E EU for selection of transfectants for RNF43+/- screening ( |
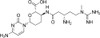
| Molecular Formula | C17H26N8O5 · HCl |
| Solubility | Clear and colorless or slight light yellow solution (5 mg/mL in H2O) |
| Impurity Profile |
LD50 i.v. in mice: 2.82 mg/kg (Takeuchi). |
| References |
Adachi H, Hasebe T, Yoshinaga K , Ohta T and Sutoh K (1994) Isolation of Dictyostelium discoideum cytokinesis mutants by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of the Blasticidin S resistance marker. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 205(3):1808-1814 Bento, FM (2004) Over expression of the selectable marker Blasticidin S deaminase gene is toxic to human keratinocytes and murine BALB/MK Cells. BMC Biotechnol. 4 (29):1-10 PMID 15575952 Izumi M et al (1991) Blasticidin S-resistance gene (bsr): A novel selectable marker for mammalian cells. Exp.Cell Res.197:229-33 Lu K-T et al (2016) Ovatodiolide inhibits breast cancer stem/progenitor cells through SMURF2-mediated downregulation of Hsp27. Toxins 8(5):127 Kim H et al (2014) A co-CRISPR strategy for efficient genome editing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 197(4):1069-1080 PMID 24879462 Kimura M, Takatsuki A, Yamaguchi I (1994) Blasticidin S deaminase gene from Aspergillus terreus(BSD): A new drug resistance gene for transfection of mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1219(3):653-65 PMID 7948022 Svidritskiy E, Ling C, Ermolenko DN, Korostelev AA (2013) Blasticidin S inhibits translation by trapping deformed TRNA on the ribosome. PNAS 110(30):12283-12288 PMID 23824292 Takeuchi S, Hirayama K, Ueda K, Sakai H and Yonehara H (1958) Blasticidin S, a new antibiotic. J. Antibiot. 11(1):1-5 PMID 13525246 Yamaguchi I et al (1990) Expression of the Blasticidin S deaminase gene (bsr) in tobacco: Fungicide tolerance and a new selective marker for transgenic plants. Mol. Gen. Genet (2):332-334 PMID 2250657 Blasticidin S Hydrochloride (TOKU-E) A DNA repair player, ring finger protein 43, relieves etoposide-induced topoisomerase II poisoning. Genes Cells. 25:718–729 PMID 32939879 |
| Protocols |
Blasticidin S HCl Kill Curve ProtocolBackground: Blasticidin S HCl is a nucleoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseochromogenes and is routinely used as a selective agent for bacterial and mammalian cells that have been transformed or transfected with plasmids containing Blasticidin resistance genes, namely bsr and BSD. Before stable transfected cell lines can be selected, the optimal blasticidin S HCl concentration needs to be determined by performing a kill curve titration. The optimal concentration of blasticidin S HCl suitable for selection of resistant mammalian clones depends on the cell lines, media, growth conditions, and the quality of blasticidin S HCl, but typically lies between 1 µg/mL - 30 µg/mL. Because of these variables, it is necessary to perform a kill curve for every new cell type and new batch of Blasticidin S HCl.Preparation and storage of Blasticidin S HCl solution:
Plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol
Once the appropriate antibiotic concentration to use for selection of the stable transfected cells has been determined by performing a kill curve, the next step is to generate a stable cell line by transfection of the parental cell line with a plasmid containing the gene of interest and an antibiotic resistance gene. Plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol:
QC Seed 24-wells with insert and determine the transfection efficiency by immunostaining:
Selection of Stable Transfected Cell Lines Protocol: Background: Once the cells have been successfully transfected, the next step is to seed and select the transfected cell line in a single 96-well plate to select pure colonies by limited dilution as outlined below: Protocol:
QC Seed 24-wells with insert for an immunostaining to determine percentage of cells expressing the gene of interest to be able to identify a 100% pure clone. You can also use Western blotting, flow cytometry or another technique depending on the cell line used. Seed 24-wells with insert and determine the expression level of the gene of interest by immunostaining:
|