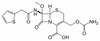
Cefoxitin Sodium, USP is the sodium salt of Cefoxitin, a cephamycin β-lactam second-generation cephalosporin that is resistant to β-lactamases. It has activity against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Cefoxitin was discovered in 1972 and developed by Merck and Lilly from Cephamycin C while they were reviewing penicillin-producing bacteria. Cephamycin C, the first cephem, but was highly resistant to several β-lactamases. It was synthesized in order to broaden its spectrum of activity to include Gram-positive bacteria, and this work included more than 300 modifications to the molecule. Cefotixin is resistance to β-lactamses is in part due to the presence of the 7-alpha-methoxy functional group.
Cefoxitin Sodium is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
We also offer:
- Cefoxitin (C091)
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephamycins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephamycins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. Like many cephamycins, Cefoxitin is resistant to β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Cefoxitin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Like many cephamycins, Cefoxitin is particularly effective against anaerobic bacteria. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Cefoxitin Sodium is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N3NaO7S2 |
| Assay | Dried Basis: 927 - 970 µg/mg (based on C16H17N3O7S2); 97.5% - 102.0% (based on C16H16N3NaO7S2) |
| References |
Georgopapadakou NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 37 (3):559-565 Onishi HR, Daoust DR, Zimmerman SB, Hendlin D, Stapley EO (1974) Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: Resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 5(1):38-48 PMID 4599124 |