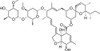
Epi-Avermectin B1a is the base-catalysed intermediate formed during decomposition of Avermectin B1a in vivo following treatment with Avermectin and is an environmental degradation product. Epi-Avermectin B1a is formed by epimerisation at the 2-position which ultimately rearranges irreversibly to the isomeric alkene analog Delta-2-Avermectin B1a. Epi-Avermectin B1a is very weakly active as a nematocide showing ~100-fold loss of biological activity compared with the parent Avermectin. There are eight Avermectin fractions designated as A1a, A1b, A2a, A2b, B1a, B1b, B2a, and B2b. The B1 fraction has the most effective antiparasitic activity.
Epi-Avermectin B1a is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Avermectins can modulate gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) chloride channels in vertebrate neurons. |
| Insect Biology Applications | Electrophysiological findings by injection of E. elegans mRNA into Xenopus laevis oocytes indicated that Avermectins act on glutamate-gated chloride channels in nematodes. |
| References |
Blizzard T, Fisher MH, Mrozik H and Shih TL (1990) Avermectins and Milbemycins. In: Lukacs G, Ohno M. (eds) Recent Progress in the Chemical Synthesis of Antibiotics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg Chen TS, Inamine ES (1989) Studies on the biosynthesis of Avermectins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 270(2):521-5 PMID 2705778 Egerton JR et al (1979) Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: Efficacy of the B1a component. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 15(3):372-378 PMID 464563 Ikeda H and Omura S (1997) Avermectin biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 97(7):2591-2610 Pivnichny JV, Arison BY, Preiser FA, Shim JSK and Mrozik H (1988) Base-catalyzed isomerization of avermectins. J. Agric. Food Chem 36(4):826-828 Pivnichny JV, Shim JK and Zimmerman LA (1983) Direct determination of avermectins in plasma at nanogram levels by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Sci. 72(12):1447-1450 PMID 6663483 |