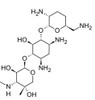
Gentamicin C1a Sulfate, EvoPure is ≥95.0% pure Gentamicin C1a. Gentamicin C1a is part of the Gentamicin C complex, along with Gentamicin C1 and Gentamicin C2, and together this complex makes up 80% of Gentamicin and has the highest antibacterial activity. Gentamicin C1a differs from Gentamicin C1 by a methyl group in the 6’ position of the purpurosamine (2-amino-hexose) ring. The antimicrobial activity of the Gentamicin complex is thought to arise from the lack of hydroxy groups on the 3’ and 4’ positions of the purpurosamine (2-amino-hexose) fragments.
EvoPure® products have been fully characterized by spectral analysis and are shipped with a comprehensive certificate of analysis containing lot-specific HPLC, MS, HNMR, and FTIR data.
We also offer:
- Gentamicin Sulfate, USP (G006)
- Gentamicin Sulfate EP (G007)
- Gentamicin Sulfate Solution (50 mg/ml in Water), (G046)
- Gentamicin A Sulfate (G035)
- Gentamicin C1 Sulfate, EvoPure (G031)
- Gentamicin C2 Sulfate, EvoPure (G033)
- Gentamicin C2a Sulfate, EvoPure (G034)
- Gentamicin C2b Sulfate, EvoPure (G062)
- Gentamicin X2 Sulfate, EvoPure (G036)
| Mechanism of Action | Aminoglycosides target the 30S ribosomal subunit resulting in an inability to read mRNA ultimately producing a faulty or nonexistent protein. |
| Spectrum | Gentamicin is a broad spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is effective against several strains of Mycoplasma. |
| Microbiology Applications | Gentamicin EvoPure compounds can be used to study effects of individual Gentamicin components on various bacterial strains.
Representative MIC values include:
|
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | HIV gene expression is dependent on binding of the viral Tat protein to the transactivation RNA response element. A number of synthetic Tat‐transactivation responsive element interaction inhibitors were described as potential antiviral drug prototypes. Researchers modified commercial Gentamicin C, specifically the purified Gentamicin C1a isomer, by attaching arginine moieties. The result was R4GC1a, a new class of peptidomimetric inhibitors. The cytotoxicity of the compound was studied in LAN 1 (human neuroblastoma), MPC11 (murine plasmacytoma) and MT4 (human T‐lymphocytes) cell cultures. There was no cell growth inhibition in culture using up to 1 mM concentration (Litovchick et al, 1999). |
| Molecular Formula |
C19H39N5O7 · xH2SO4 (lot specific) |
| References | Davis, BD (1987) Mechanism of bactericidal action of aminoglycosides. Microbiol. Rev. 51(3): 341-350 PMID 3312985 Stypulkowska K, Blazewicz A, Fijalek Z, Sarna K.(2010) Determination of Gentamicin Sulphate composition and related substances in pharmaceutical preparations by LC with charged aerosol detection. Chromatograph. 72(11-12):1225-1229 PMID 21212825 Vydrin, AF (2003) Component composition of Gentamicin Sulfate preparations. Pharma. Chem. J 37(8): 448-449 Weinstein, MJ, Wagman GH, Oden EM and Marquez JA (1967) Biological activity of the antibiotic components of the Gentamicin complex. J. Bacteriol. 94(3):789-790 PMID 4962848 |
| MIC | Bacillus subtilis| 6|| Escherichia coli| 12 - 96|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 12 - 384|| Staphylococcus epidermidis| 6|| Mycobacteria | 8 - 64|| Mycobacterium aurum| 0.06 - >256|| Mycobacterium avium| 1 - 100|| Mycobacterium bovis| 0.05 - 0.25|| Mycobacterium chelonae | >32|| Mycobacterium fortuitum| 0.25 - 2|| Mycobacterium gordonae| 8|| Mycobacterium intracellulare| 6.25 - 100|| Mycobacterium kansasii| 2 - 4|| Mycobacterium paratuberculosis| 0.025 - 0.05|| Mycobacterium phlei| 2 - 4|| Mycobacterium scrofulaceum| 0.5 - 2|| Mycobacterium smegmatis| 1 - 4|| Mycobacterium tuberculosis| 0.0125 - 20000|| Mycobacterium vaccae| 0.5|| Mycobacterium xenopi| 0.125 - 2|| |