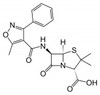
Oxacillin Sodium, USP is the sodium salt of Oxacillin, semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant and acid-stable antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic primarily used against Gram-positive organisms. It can be used to study autolysins and mechanisms of penicillinase resistance.
| Mechanism of Action | β-lactams interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to β-lactams is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. Oxacillin however, is resistant to the degradative effects of β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Oxacillin is used primarily against Gram-positive organisms namely resistant Staphylococcus species. |
| Microbiology Applications | Oxacillin Sodium is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
Media SupplementsOxacillin can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media: ORSAB - ORSAB Selective Supplement |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18N3NaO5S (anhydrous basis) |
| References |
Fox et al. used Oxacillin Sodium (TOKU-E) to study its synergistic effects with blue light irradiation against Staphylococcus aureus. "Investigating inhibitory synergy between blue light irradiation and antibiotic treatment of Staphylococcus aureus." Pitout JD, Sanders CC, Sanders WE Jr. (1997) Antimicrobial resistance with focus on beta-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Am. J. Med 103:51 |
| MIC | Diplococcus pneumoniae| 0.003 - 0.2|| Haemophilus influenzae| 6.3 - 50|| |