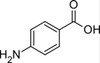
4-Aminobenzoic Acid (syn: PABA) is a B-vitamin derivative and is used by bacteria to synthesize folate (vitamin B9), an essential vitamin for bacteria and humans. This compound is an aminobenzoic acid in which the amino group is para to the carboxy group. It functions as an Escherichia coli metabolite, a plant metabolite and allergen. Functionally, it is related to benzoic acid.
PABA is used in biomedical applications since its derivatives can be found as a structural component in commercial pharmaceutical compounds. It can be converted to azo dyes and crosslinking agents. PABA photodegrades via an oxygen-mediated pathway where PABA is oxidized via hydrogen abstraction and decarboxylation (Ref 14).
4-Aminobenzoic Acid, USP is slightly soluble in water.
| Impurity Profile | Volatile Diazotizable Substances: Not more than 0.002% Ordinary Impurities: Not more than 1.0% Limit of Aniline: Not more than 10 ppm Limit of p-Toluidine: Not more than 10 ppm |
| Microbiology Applications | Folate (vitamin B9) plays an essential role in the synthesis, repair, and methylation of DNA. In addition, many sulfonamide antibiotics inhibit dihydropteroate synthetase, an enzyme involved in the folate synthesis pathway. |
| Plant Biology | Plants produce PABA in their chloroplasts, and store it as a glucose ester (pABA-Glc) |
| References |
Basset G (2004) Folate synthesis in plants: The P-aminobenzoate branch is initiated by a bifunctional PabA-PabB protein that is targeted to plastids. PNAS 101.6 (2004): 1496-501 Richter MK, Focks A, Siegfried B, et al. Identification and dynamic modeling of biomarkers for bacterial uptake and effect of sulfonamide antimicrobials. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987). 2013 Jan;172:208-215. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.09.011. PMID: 23063996. Zhang S et al (2016) Unveiling self-sensitized photodegradation pathways by DFT calculations: A case of sunscreen p-aminobenzoic acid. Chemosphere. 163:227-233 PMID 27529387 |