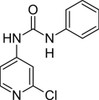
4-CPPU (CPPU) is a highly active plant growth regulator of the cytokine class that increases chlorophyll biosynthesis, cell division and cell expansion. It can increase fruit set and fruit enlargement and promote somatic embryogenesis. It works synergistically with the plant's endogenous auxin levels to increase plant growth. In mammalian systems, it has anti-mitotic and anti-migratory properties and could be a promising septin-based anti-tumor agent. It can also be used to study septin biology. 4-CPPU is a cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKO) inhibitor.
4-CPPU is soluble in ethanol and methanol.
This product is considered a dangerous good. Quantities above 1 gram may be subject to additional shipping fees. Please contact us for questions.
| Application | 4-CPPU is a promising tool to study function and organization of mammalian septins and septin biology. It could also be considered as a septin-based anti-tumor agent due to its anti-mitotic and anti-migratory properties. |
| Mechanism of Action | 4-CPPU is a cytokinin oxidase inhibitor, which regulates cytokinin activity. It can also promote carbohydrate mobilization and modify the balance among endogenous plant growth regulators. 4-CPPU is a cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKO) inhibitor. |
| Plant Biology Applications | 4-CPPU has been used as a media supplement for citrus to enhance somatic embryogenesis from stigma and style cell layer explants (Fiore et al, 2002). Somatic embryos arose from callus at the surface of stima and style for sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) and lemon (Citrus limon), with embryo formation ranging from 0% (2,4-D) to 16% (4-CPPU) for Iemon.
The effect of 4-CPPU on fruit development was studied in young macadamia fruit. The compound reduced young fruit drop and delayed fruit drop by mobilizing carbohydrates from the leaves to the fruits, resulting in an increase in total soluble sugars and starch in the bearing shoots and soluble sugars in the seeds. 4-CPPU reduced early fruit drop by increasing carbohydrate availability and modifying the balance among endogenous hormones (Zeng et al, 2016). 4-CPPU was found to enhance in vitro direct shoot organogenesis from epicotyl segments of sour orange (Citrus aurantium). This compound could be valuable in citrus genetic transformation protocols as it resulted in 100% direct shoot organogenesis when used at 0.05 mg/L when combined with 0.2 mg/L IAA (Roussos et al, 2011). |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | 4-CPPU is a bioactive small molecule that can alter septin assembly in vitro without affecting actin or tubulin polymerization. Using mammalian septins and a recombinant SEPT2/6/7 as an in vitro septin assembly system, authors found 4-CPPU directly altered septin assembly in vitro. Treated cells displayed mitosis defects that phenocopy the effects of septin knockdown by siRNAs. Septins are found in many eukaryotes ranging from fungi to animals. In mammalian cells, they regulate cytoskeleton organization and are needed for chromosome alignment /segregation during mitoisis and thus they are implicated in cancer and neuropathies (Hu et al, 2008). |
| References |
Curry EA and Greene DW (1993) CPPU influences fruit quality, fruit set, return bloom, and preharvest drop of apples. HortSci. 28(2):115-119 Hu Q, Nelson WJ and Spiiotis ET (2008) Forchlorfenuron alters mammalian septin assembly, organization, and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 283(43): 29563–29571 PMID 18713753 |