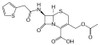
Cephalothin Sodium, USP is a semisynthetic, β-lactam, first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. It is effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Cephalothin Sodium is inactivated by cephalosporinase.
Cephalothin Sodium is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Cephalothin Sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria especially those which cause respiratory and skin infections. |
| Microbiology Applications | Cephalothin Sodium is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
Media SupplementsCephalothin can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media: Columbia Blood Agar - Campylobacter selective supplement (Blaser-Wang) |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | In vitro cytotoxicity test for estimating the non-ocular irritation dose of ophthalmic solutions was studied using human epidermal keratinocytes in a monolayer. This system can estimate non-ocular irritation dose in advance of the in vivo tests (Nagami and Maki, 1993). Cephalothin resistance in E. coli was found to be mediated by OxyS RNA, a small non-coding RNA which is induced in response to oxidative stress. OxyS modulates gene expression in multiple pathways to develop resistance. In fact, 17 CRP-associated pathway genes are involved. (Cho and Kim, 2018). |
| Molecular Formula | C16H15N2NaO6S2 |
| Impurity Profile | Chromatographic Purity: Individual Impurity: ≤ 1.0% Total Impurities: ≤ 3.0% |
| Impurities | Individual Impurity: ≤1.0% Total Impurities: ≤3.0% |
| References | Cho H and Kim K (2018) Escherichia coli OxyS RNA triggers Cephalothin resistance by modulating the expression of CRP-associated genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm 506(1):66-72 PMID 30340824 Georgopapadakou, NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of Cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37(3): 559-565 Nagami K, Maki E (1993) In vitro cytotoxicity test for estimating non-ocular irritation dose of ophthalmic solutions. Cell Biol and Toxicol 9(2):107-118 PMID 8242427 |
| MIC | Diplococcus pneumoniae| 0.01 - 0.8|| Haemophilus influenzae| 3.1 - 25|| Neisseria gonorrhoeae| 0.03 - 8|| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia| >128|| |