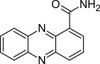
Oxychloroaphine (1-phenazinecarboxamide) is a simple phenazine produced by many species of Pseudomonas. It is a antifungal involved in plant biocontrol with activity against Pseudomonas. Oxychloroaphine and related phenazines are used as standards in discovery research to eliminate leads due to high amounts of weakly potent actives.
Oxychloroaphine is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Poor water solubility.
| References |
Blankenfeldt W (2013) The Biosynthesis of Phenazines. In: Chincholkar S, Thomashow L (eds) Microbial Phenazines. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi. 10.1007/978-3-642-40573-0_1 Hays EE et al (1945) Antibiotic substances produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 159:725-750 |