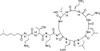
Polymyxin E2 Sulfate, EvoPure (syn: Colistin B) is one of the two major components of Polymyxin E (Colistin). Polymyxin E1 and E2 are structurally similar and differ only by a fatty acid group at the N-terminus. Polymyxin E1 contains 6-methyloctanoic acid and Polymyxin E2 (Colistin B) contains 6-methylheptanoic acid. Together, Polymyxin E1 and E2 comprise approximately 85% of Polymyxin E; however, 13 different Polymyxin E components have been indentified.
We also offer:
- Polymyxin B Sulfate, USP (P007)
- Polymyxin B1 Sulfate, EvoPure (P037)
- Polymyxin B1-I Sulfate, EvoPure (P038)
- Polymyxin B2 Sulfate, EvoPure (P039)
- Polymyxin B3 Sulfate, EvoPure (P040)
- Polymyxin B6 Sulfate, EvoPure (P054)
- Polymyxin E1 Sulfate, EvoPure (P055)
- Polymyxin E2 Sulfate, EvoPure (P056)
EvoPure products are purified single antibiotic fractions, most are >99% pure. Highly pure EvoPure Polymyxin products can be used to analyze the specific effects of individual Polymyxin B fractions.
| Mechanism of Action | Polymyxin E has a bactericidal effect on Gram-negative bacteria by interacting with and displacing essential ions in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer cell wall leading to increased permeability and eventually lysis and death of the cell. |
| Spectrum | Polymyxin E is used primarily against Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and multi-drug resistant Enterobacteriaceae, |
| Microbiology Applications | Polymyxin E1 and E2 (Colistin A and B, respectively) can be used individually to study and compare in vitro antimicrobial activity with colistin (polymyxin E complex) or other polymyxins. |
| Molecular Formula | C52H98N16O13 · xH2SO4 (lot specific) |
| References |
Bergen, PJ, Craig JL, Rayner CR and Nation RL (2006) Colistin methanesulfonate is an inactive prodrug of Colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicob. Agents Chemother. 50(6):1953-1958 PMID 16723551 Decolin D, Leroy P, Nicolas A and Archimbault P (2013) Hyphenated liquid chromatographic method for the determination of colistin residues in bovine tissues. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 35(12):557-564 PMID 9397540 Falagas ME and Kasiakou SF (2005) Colistin: The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis.40(9):1333-1341 PMID 15825037 Leifert C, Ritchie JY and Waites WM (1991) Contaminants of plant-tissue and cell cultures. World J. Microbiol. and Biotechnol. 7:452-469 PMID 24425131 Li J and Nation RL (2006) Comment On: Pharmacokinetics of inhaled colistin in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58(1):222-223 PMID 16641116 Muellerr MJ, Brodschelm W, Spannagl E and Zenk MH (1993) Signaling in the elicitation process is mediated through the octadecanoid pathway leading to jasmonic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(16):7490-7494 PMID 11607420
|